How Digitalization Can Enhance Economic Resilience
by Alexander Copestake , Julia Estefania Flores , Davide FurceriLinkedIn Digital Development Jobs and Development
The COVID-19 crisis has opened deep economic scars, leading to significant output losses. Can digitalization improve economic resilience to shocks such as the pandemic? The International Monetary Fund’s Asia-Pacific Department leveraged LinkedIn data to examine the role of digitalization in supporting resilience in employment during the health crisis.
Challenge
During the COVID-19 pandemic, governments, firms, and individuals had to adapt to lockdowns and social distancing measures that have had deep and lasting effects on work and consumption practices. This health crisis resulted in large and persistent output losses across the world, known as scarring.
However, this health crisis also drove the rapid adoption of new digital technologies, from teleconferencing software to e-commerce platforms. Digitalization became an important channel to mitigate harm from pandemic- response measures. Many companies transformed their work practices, offering employees hybrid work models and offering customers contactless transactions. Digital skills were essential for both firms and employees to build resilience to recessions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.

Solution
As digital skills have become increasingly important, a trend accelerated by the pandemic, it is crucial to understand their impact on the labor market. The International Monetary Fund’s Asia-Pacific Department leveraged LinkedIn data on skills penetration, career transitions, and hiring rates.
The team revealed that digitalization supported resilience in employment: hiring rates were higher in industries using more digital skills, and those industries also attracted larger net inflows of workers.
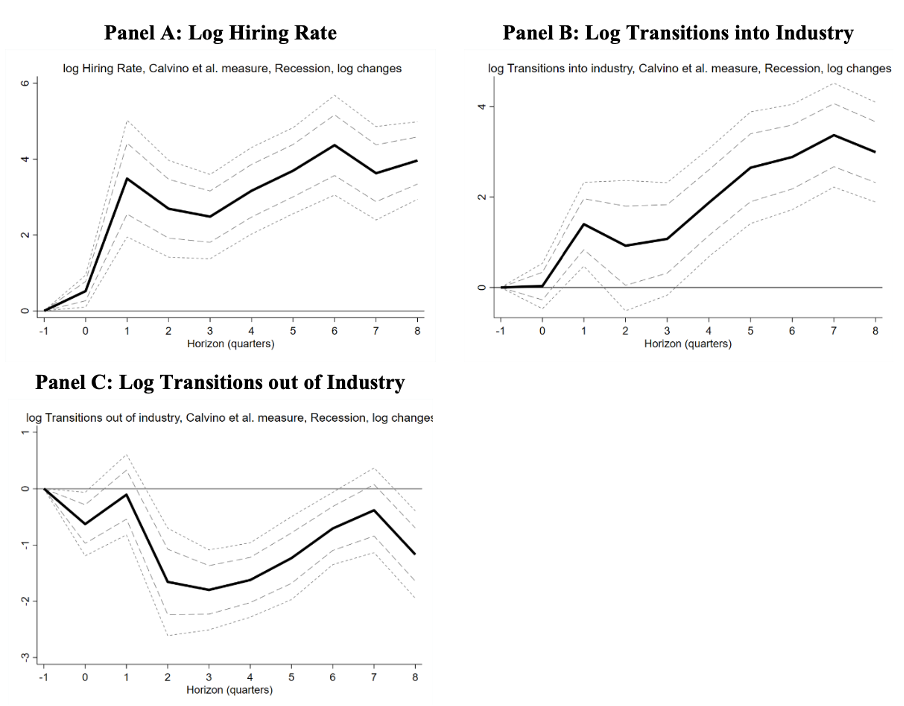
Hiring rates are calculated using the share of LinkedIn members adding a new employer to their profile in the same month that the job begins, and digital skills usage is calculated using the proportion of such skills listed by users within a particular country-industry pair.
Figure 1 shows the differential effect of COVID-19 recessions on growth in hiring rates and total transitions by workers into and out of each industry, using industry-level outcome variables from LinkedIn. Panel A shows that hiring rates in highly digitalized industries grew almost 3 percent faster than in average industries in the year after the COVID-19 recession, and almost 4 percent faster after two years. Similarly, Panel B shows that the inflow of workers to highly digitalized industries grew more than 3 percent faster than in other industries in the two years after the shock, while Panel C shows that the outflow of workers from highly digitalized industries was 1 percent slower in those two years.
Impact
Digitalization can be a powerful force in mitigating scarring. Drawing on the LinkedIn data, the International Monetary Fund found that more digitalized industries had higher hiring rates in the two years after pandemic-induced recessions, and experienced greater net inflows. These key results highlight the significant role of digitalization in mitigating scarring and improving firm resilience.
As digitalization can help reduce the harmful effects of economic downturns, this study provides support for efforts to promote the widespread adoption of digital technologies to mitigate scarring, including support for re-training and upskilling programs to help both employees and firms build resilience to future shocks.